North America's hardwood forests are thriving thanks to responsible forest management. U.S. hardwoods grow more rapidly than they are harvested, ensuring a renewable supply for future generations. This sustainable growth benefits both the environment and the hardwood industry.
Updated for accuracy and expanded to reflect current sustainability data and industry standards.
Introduction: Why North American Hardwoods Are Truly Sustainable
Despite concerns about deforestation globally, North America’s hardwood forests remain not only intact but thriving. In fact, the total volume and area of hardwood forests in the U.S. and Canada have steadily increased over the last several decades. Moreover, these ecosystems serve as trusted carbon sinks, support biodiversity, and form the backbone of responsible rural forestry economies.
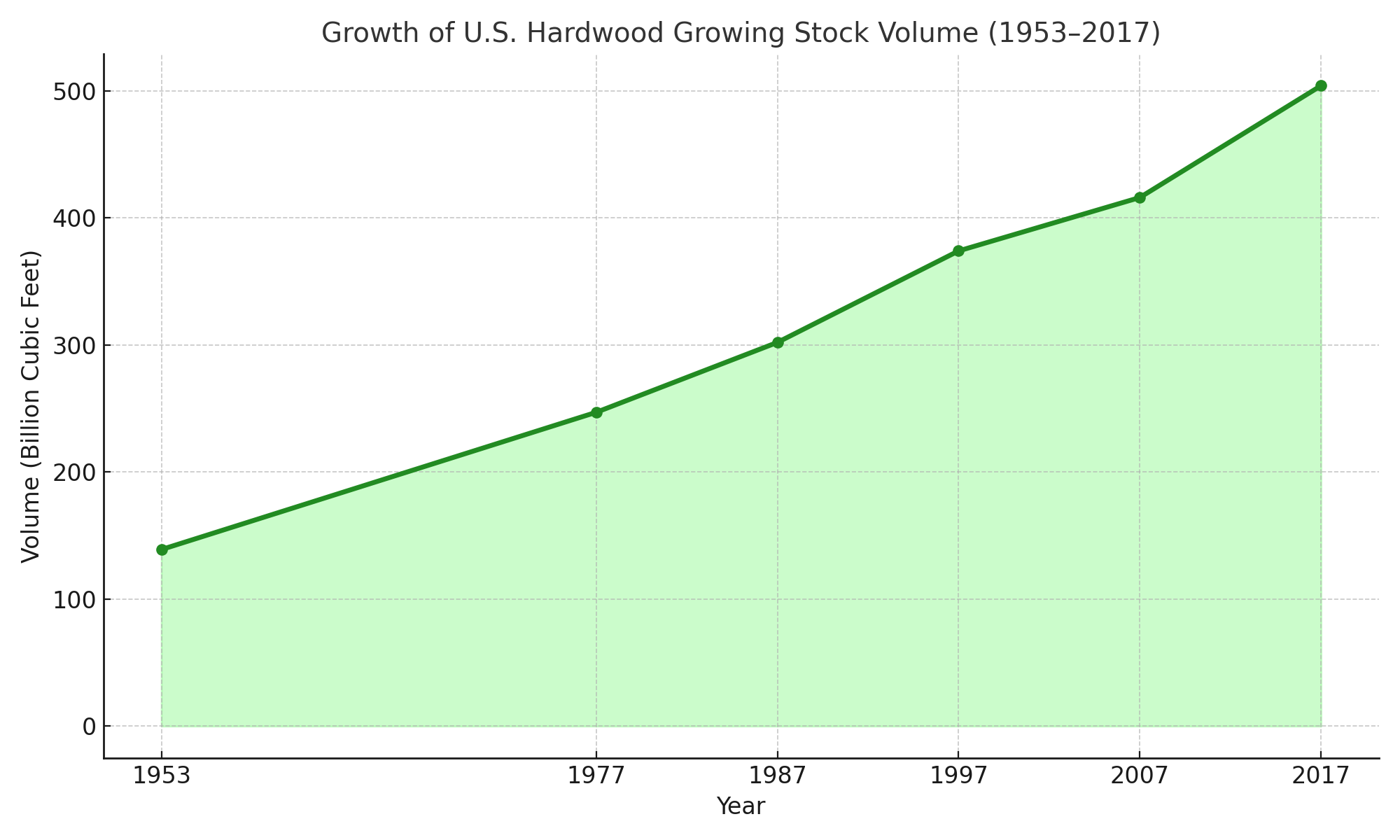
Forest Growth vs. Harvest: Positive Trends Over Time
From 1953 to 2017, U.S. hardwood growing stock nearly doubled—from about 5.2 billion m³ to 12.0 billion m³. During that period, area of hardwood and mixed hardwood forests expanded from 99 million hectares to 117 million hectares—an increase of roughly 280,000 hectares per year. Notably, large-diameter hardwood volume (≥48 cm) grew nearly fourfold in that same timeframe.
Forest Ownership & Harvest Practices
Approximately 89% of hardwood harvests in the U.S. come from privately owned lands. With more than 9.7 million private forest owners, each managing modest acreage, harvesting typically occurs once per owner’s lifetime. Harvesting prioritizes mature trees using careful methods such as single-tree selection, rather than clear-cutting. As a result, natural regeneration—occurring on 97% of hardwood lands—is common and sustainable.
Certification & Responsible Sourcing
Third-party forest certification systems—including the Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI), Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), and American Tree Farm System (ATFS)—play a critical role in ensuring sustainable practice. The SFI 2022 standard alone now covers over 370 million acres in North America, with rigorous standards in biodiversity protection, sustainable harvest levels, chain-of-custody tracking, and climate-smart forestry planning.
Carbon Sequestration & Climate Benefits
Hardwood trees naturally absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere and store that carbon in their biomass. When harvested and used as lumber or furnishings, that carbon remains locked in for decades, sometimes even centuries. According to global reviews, substituting hardwood for more carbon-intensive materials like concrete or steel can reduce CO₂ emissions by 0.75–1 ton per cubic meter of wood used.
Environmental & Economic Benefits
Hardwood products offer a sustainable alternative with significant environmental and economic advantages:
- Low carbon footprint manufacturing: Wood requires far less energy to produce compared to concrete, steel, or aluminum.
- Long life cycle: Hardwood installations in homes or offices can endure for decades or generations with minimal maintenance.
- Certified returns: Choosing certified hardwood incentivizes forest management that supports wildlife, water quality, and rural economies.
Summary & Resources
North American hardwood forests are a model of sustainable forestry: growing faster than they are harvested, managed under third‑party standards, environmentally regenerative, and economically valuable. Whether sourced as sawlogs, veneer, flooring, or export-grade lumber, responsibly harvested hardwood supports both ecological health and industrial supply chains.
To explore these sustainability metrics in greater detail—including interactive data on forest volume, growth, and yield—visit the American Hardwood Export Council’s sustainability page.


Comments 1
Unfortunately I only have one red oak and seven hickory the oak is every bit of 34″ across and 75′ to 80′ to its first limb … The hickory have bout 12- 16 inches across each crocheted bout 18′ to 30′ from ground resulting in 2 state trunks. I tried estamating the board ft of the oak going from the chart provided on ur site has every bit of 1590′ is that fair to say? Then the hickory just may be to small compared to the oak. I don’t have much knowledge of value and volume. But i would be more then willing to send photos via smart phone or via email. Please contact me about the timber. The trees have been here long before the house and the house was built mid 1930 there is no metal or foreign materials in the tree. I would rather receive a txt the email 3307347395 thank you for the insight of all of whats behind foresty